
The fixed cost will be reduced in comparison to the cost of each unit made, enhancing your profit margin for that product. A variable cost is a specific material utilized in production because the price increases as you order more. Bulk orders are frequently discounted, introducing a variable into your incremental calculation. In other words, incremental costs are exclusively determined by the amount of output.
- For discrete calculation without calculus, marginal cost equals the change in total (or variable) cost that comes with each additional unit produced.
- Management must look at these incremental costs and compare them to the additional revenue before it decides to start producing the new product.
- If a reduced price is established for a special order, then it’s critical that the revenue received from the special order at least covers the incremental costs.
- They are both decrease at first with the increase of output, then start to increase after reaching a certain scale.
Ways a Digital Lending Platform Can Elevate Your Business
- In this post, we define incremental cost, learn how to calculate it with a formula and see an example of how it might assist a business make profitable decisions.
- So, you get a profit of $4,000,000 by deducting the incremental cost from the incremental revenue.
- If a reduced price is established for a special order, then it’s critical that the revenue received from the special order at least covers the incremental costs.
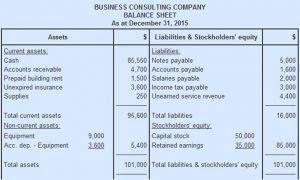
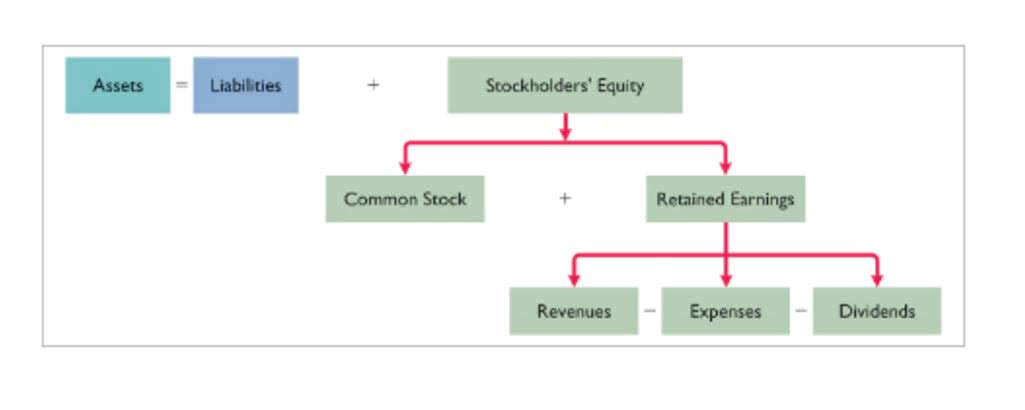
- Incremental cost, also referred to as marginal cost, is the total change a company experiences within its balance sheet or income statement due to the production and sale of an additional unit of product.
For example, it may not always accurately reflect the true cost of production, as some costs may be fixed regardless of how many units are produced. Additionally, incremental cost analysis does not consider opportunity costs, which are the potential benefits that are forgone when one course of action is chosen over another. As a result, decision-makers should use caution when relying on it’s analysis and should consider all relevant factors before making a decision. If a reduced price is established for a special order, then it’s critical that the revenue received from the special order at least covers the incremental costs.
RESTRICTED CASH: Definition & Its Financial Statement
Understanding incremental expenses can assist a business in improving its efficiency and saving money. Incremental costs can also help you decide whether to make a product or buy it elsewhere. Understanding the additional costs of increasing a product’s manufacturing is beneficial when deciding the retail price of the product. Companies seek to maximize production levels and https://www.bookstime.com/ profitability by analyzing the incremental costs of manufacturing. When evaluating a business segment’s profitability, only relevant incremental costs that can be directly linked to the business segment are examined. From the above information, we see that the incremental cost of manufacturing the additional 2,000 units (10,000 vs. 8,000) is $40,000 ($360,000 vs. $320,000).
Benefits to Incremental Cost Analysis
As a result, while both ideas are related to a cost shift, marginal cost relates to both a rise and a decrease in production. For example, unearned revenue while a monopoly has an MC curve, it does not have a supply curve. In a perfectly competitive market, a supply curve shows the quantity a seller is willing and able to supply at each price – for each price, there is a unique quantity that would be supplied. Incremental cost of capital is related to composite cost of capital, which is a company’s cost to borrow money given the proportional amounts of each type of debt and equity a company has taken on. Composite cost of capital may also be known as weighted average cost of capital.

Investing in Gold: How to Secure Your Wealth in Uncertain Times
For example, if you normally produce 10,000 units of a product per month, this base monthly volume is 10,000 units. For the past 52 years, Harold Averkamp (CPA, MBA) hasworked as an accounting supervisor, manager, consultant, university instructor, and innovator in teaching accounting online. For the past 52 years, Harold Averkamp (CPA, MBA) has worked as an accounting supervisor, manager, consultant, university instructor, and innovator in teaching accounting online. The base case is your existing or normal volume level before any proposed volume increase. The company is not operating at capacity and will not be required to invest in equipment or overtime to accept any special order that it may receive.

What is incremental cost and how is it calculated
For instance, evaluating expanding monthly production from 10,000 units to 15,000 units means the incremental change is 5,000 units. The incremental volume change is how much extra output is being proposed or considered for evaluation. One advantage of using this is that it provides information about whether it is efficient to produce more units of a good or service. It can also help managers make decisions about how many resources to allocate to different activities. Another advantage is that it can help decision-makers compare the costs and benefits of different courses of action.
Terms Similar to Incremental Cost
However, the $50 of allocated fixed overhead costs are a sunk cost and are already spent. Therefore, the cost to produce the special order is $200 per item ($125 + $50 + $25). In the above formula, the total cost of increased production refers to the previous volume and the new units added to it. However, none of it will include the fixed costs since they will not change due to volume fluctuation. To improve decision-making efficiency, incremental cost calculation should incremental cost be automated at all levels of production.